Accounting refers to the “language of business” and understanding its core principles is essential for anyone involved in finance or business management. In this article, you will learn the basics of accounting concepts and principles as a framework for financial reporting and how they form the foundation for accurate financial reporting.
Here are the topics we will cover:
- What accounting concepts mean.
- What accounting principles mean.
- Importance of accounting concepts and principles.
Before we start, you have to read about what accounting is and how it works in this article. Let’s move on to the next section to understand accounting principles.
What are Accounting Principles?
Accounting principles are the standardized rules and guidelines that govern the field of accounting.
They ensure many things, such as consistency, transparency, and comparability of financial statements across organizations. These principles are very important for accurate financial reporting and decision-making. Below are the key accounting principles:
- 1. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
- 2. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- 3. Basic Accounting Principles
Here is a brief explanation for each key in accounting principles:
Accrual Principle
The accrual principle means that a business has to account for earned and spent cash at the moment the cash is earned or spent instead of when actual cash changes hands.
This improves the accuracy of the business’s financial position. For instance, a business records the sale on the day the order is shipped even if payment is made at a later date.
Consistency Principle
The consistency principle means that a company must apply the same accounting policies and methods throughout the years without changing them. This allows for comparison across different periods.
If a change in method is warranted, then it needs to be justified.
Conservatism Principle
The conservatism principle indicates the need for caution when preparing the financial statements of the business.
When an accountant is not certain of particular gains, these should be left out, yet losses can happen. This is often used to avoid the creation of fictitious profits.
Cost Principle
The cost principle suggests that a business must maintain records of an asset on the balance sheet at the original purchase price rather than the current value estimation.
This ensures clarity in records irrespective of any fluctuations in the asset’s value in the future.
Economic Entity Principle
The economic entity principle makes sure that the financial resources of a business unit are separate from those of an owner and any other business.
Thus, it makes sure that the financial reports presented are accurate and only pertain to the business in question.
Matching Principle
The matching concept states that business expenses should be incurred at the same time as the income is received.
This will enable a business to show its actual profit in its financial statements.
Full Disclosure Principle
The principle of full disclosure suggests that every significant piece of information that will affect the financial report of a business should be presented within the report.
This will assist greatly in knowing the true financial standing of the organization.
Going-concern Principle
The going concern assumption states that the entity is assumed to continue operations in the foreseeable future.
This is the reason why assets and liabilities can be assumed at their value rather than what they would fetch if the business had to sell off everything in a hurry.
Monetary Unit Principle
The monetary unit assumption states that the recording and reporting of financial events should be done in a reasonable and stable currency, such as dollars or euros.
This also helps eliminate the issue of inflation or depreciation and allows for easy comparison of financial statements.
Reliability Principle
The reliability principle is that financial information must be accurate, unbiased, and based on proof, like invoices or contracts. This ensures that financial reports can be trusted.
Time Period Principle
The time period principle means businesses must prepare financial reports for set time periods, like monthly, quarterly, or yearly. This helps people track performance and compare results over time.
Revenue Recognition Principle
The revenue recognition principle means a business should record revenue when it is earned, even if the cash hasn’t been received yet. This helps show the company’s true performance for a specific time period.
Objectivity Principle
The objectivity principle means financial data should be based on real proof, like receipts or invoices, not personal opinions or guesses. This helps keep financial reports accurate and trustworthy.
What Are Accounting Concepts?
Accounting concepts can be defined as the basic rules that enable companies to record and report their financial activities. Also, to ensure that information is organized and easy to understand.
They are also used to help them prepare financial statements and manage transactions. They are a standard way to track key elements such as income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
Let’s look at each one of the key concepts and principles of accounting in-depth:
Going-concern concept
Financial statements are usually prepared with the idea that a company will keep running for the foreseeable future. This is called the going concern principle.
It means that the business isn’t planning to shut down or cut back its operations significantly.
But if a company is likely to close down or scale back its operations drastically, financial statements need to be prepared differently. In such cases, the alternative method used must be clearly stated.
Here is an example:
Ema bought a vehicle for her business. She paid $4,00,000 from the $6,00,000 as an invested amount. She also spent $60,000 on transport and setup.
If she continues the business, her financial status will be:
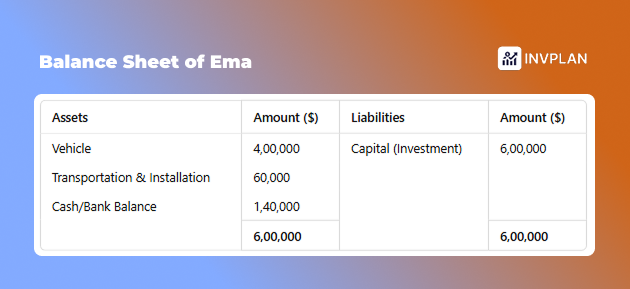
But if she decided to sell the car, the car would be worth more or less than $4,00,000. That will alter her financial position.
However, the going concern concept does not consider short-term changes in an asset’s value.
It is presumed in this concept that assets are retained to obtain future benefits and not for resale soon.
Any increase or decrease in value is not real income or loss. The balance sheet will continue to show the original price of the car to maintain consistency in financial reporting.
Accrual Concept
The accrual concept records revenue and expenses when they happen, not when cash is received or paid. This helps measure income and track assets and debts.
Accrual-based financial statements show more than past cash flow. They also reveal future cash obligations and expected income.
You have to understand revenue and expenses first to grasp the accrual concept.
- Revenue is the total inflow of cash or other benefits from:
- Selling goods,
- Providing services
- Allowing others to use the company’s resources, like earning interest, royalties, or dividends.
- Expenses are costs incurred to
- Operate the business during an accounting period.
- Generate revenue.
- Provide benefits that do not extend beyond the current period.
Revenue example:
John started a clothing business by investing $80,000. He bought merchandise worth $70,000 and sold it for $90,000. Customers paid him $75,000 in cash and promised to pay the remaining $15,000 later. John’s total revenue is $90,000, which includes $75,000 in cash and $15,000 as receivables.
Here is an example of expenses:
David purchased a machine with a useful life of 10 years. As a result, he records $12,000 per year as an expense for the machine’s cost.
Let’s see an example that includes both revenue and expense:
Emma spent $50,000 on clothing and paid $20,000 in cash. She sold it for $75,000. Customers paid $60,000 upfront and still owe $15,000.
Let’s analyze this example by following the below formula:
Revenue – Expenses = Profit
- Her revenue is $75,000 (not just the $60,000 cash received).
- Her expense is $50,000 (not just the $20,000 cash paid).
- Therefore, her profit under the accrual concept is $25,000 ($75,000 revenue – $50,000 expense).
Consistency Concept
A company should apply the same accounting principles annually so that its financial reports remain readily comparable. Changes should be made only in extraordinary circumstances.
This is important when deciding between standard practices, such as depreciation strategies or inventory pricing.
Once a method is selected, it must be applied consistently. It may sometimes appear that there is a change, but the same rule is being applied. For instance, inventory valuation at “cost or market price, whichever is lower” might result in using cost in one year and market price in another year. This still applies the rule and, therefore, is not inconsistent.
However, consistency does not mean that a firm’s methods cannot be improved. A firm must modify its accounting principles when:
- Accounting Standards require it.
- The law mandates it.
- A revised approach provides a better and more accurate financial representation.
Materiality Concept
It helps accountants to ignore certain accounting concepts if the impact is insignificant.
This principle is an exception to the full disclosure rule, meaning that only information with a significant economic effect on the business should be included in financial statements.
So, if an item is not big enough to affect decision-making but would increase the workload of the accountant, it does not need to be reported.
Materiality is a subjective concept, meaning accountants use their judgment and common sense to decide what is important.
For example, office supplies purchased but not fully used within a year are still recorded as expenses.
Small assets like calculators or books are generally depreciated in the year of purchase, though they are durable.
The importance of an item depends on some factors, such as the size of the business, the type of information, and the decision-maker’s perspective.
Prudence (Conservatism) Concept
Accountants have to deal with uncertainties such as:
- Whether customers will pay their bills.
- How long equipment will last
- How many warranty claims will be filed when preparing financial statements.
They can handle these risks by being careful when they estimate financial amounts.
Prudence means exercising care and avoiding overvaluing assets or revenues to look bigger than they are or overvaluing liabilities and expenses to look smaller.
Prudence should not be used to hide profits, create unnecessary reserves, or report lower assets or higher expenses intentionally. That would make the financial statements unreliable and misleading.
Business Entity Concept
The business entity concept means that a business should be kept separate from its owner and other businesses.
This is why a company keeps its financial records without including the assets or debts of its owner or other companies.
Financial records would be a mess, and it would be hard to track a business’s profit without this rule. Here is an example:
A business owner buys an office building personally and rents space to their own company for $12,000 a month. For the business, this is a real expense, while for the owner, it counts as taxable income.
Money Measurement Concept
The monetary measurement concept means that a company records only those transactions that can be measured in money. This means accounting focuses more on numbers than on non-financial factors.
So, many things are never recorded in a company’s books and do not appear in its financial statements.
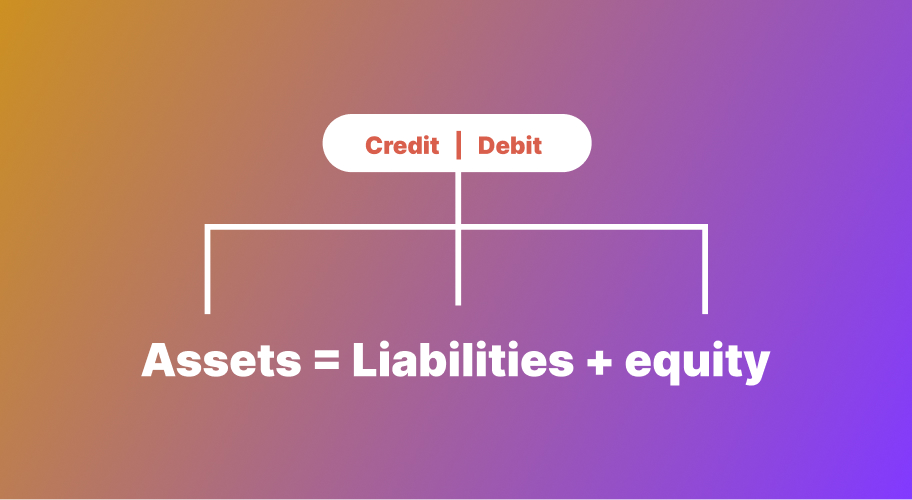
Dual Aspect Concept
It is known as the double-entry system, a basic rule for recording financial transactions correctly and consistently. It means that every transaction affects at least two accounts—one account is debited, and another is credited with the same amount.
Let’s move on to the following section to understand the importance of the accounting concepts and principles.
Importance of Accounting Concepts and Principles
They ensure that financial information is presented in a consistent, transparent, and reliable manner.
These principles are essential to help companies maintain the integrity of financial statements and foster trust among stakeholders.
Below are the key reasons why accounting concepts and principles are very important:
1. Ensures Consistency and Comparability
They confirm that financial statements are prepared using the same methods and standards over time.
This allows stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and analysts to compare financial performance across different periods and even between companies.
2. Improves Transparency and Reliability
Transparency and reliability are cornerstones of financial reporting. Accounting principles such as the accrual basis of accounting and the principle of full disclosure.
3. Facilitates Decision-Making
Financial statements are important because they help people like investors, lenders, and managers make big decisions.
Accounting rules make sure the financial information is accurate and up-to-date so these decisions can be made wisely.
4. Compliance with Regulations
These standards provide rules for financial statement creation that meet legal and regulatory requirements.
Wrapping Up
You have studied concepts and principles together with definitions and significance in financial reporting. These fundamentals give consistency, transparency, and reliability to financial reports. It aids decision-making by companies and regulatory compliance.
Here are keys of accounting principles:
- Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
- International financial reporting standards (IFRS)
- Accrual principle
- Consistency principle
- Conservatism principle
- Cost principle
- Economic entity principle
- Matching principle
- Full Disclosure principle
- Going-concern principle
- Monetary unit principle
- Reliability principle
- Time period principle
- Revenue recognition principle
- Objectivity principle
FAQ’s
What are the fundamental accounting concepts and principles?
How does the accrual basis of accounting differ from the cash basis?
Why is the matching principle important in financial reporting?
What is the significance of the revenue recognition principle?
How do Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) differ?
- GAAP is more rule-based, while IFRS is more principles-based.
- GAAP follows strict guidelines for revenue recognition, whereas IFRS allows for more judgment.
- IFRS permits inventory valuation using only FIFO or weighted average methods, while GAAP allows LIFO as well.