No standard covers all accounting work in one approach. So many businesses such as governments and non-profits all have different financial needs. Some need clear financial reports for investors. Others focus on tracking project costs or following tax laws. That’s why accounting has different types; each one serves a specific purpose.
In this article, we will cover the following topics:
- Major types of accounting.
- Specialized accounting fields.
- Choosing the right type of accounting for your business.
Before we get started, read about what accounting is, its principles, and its concepts.
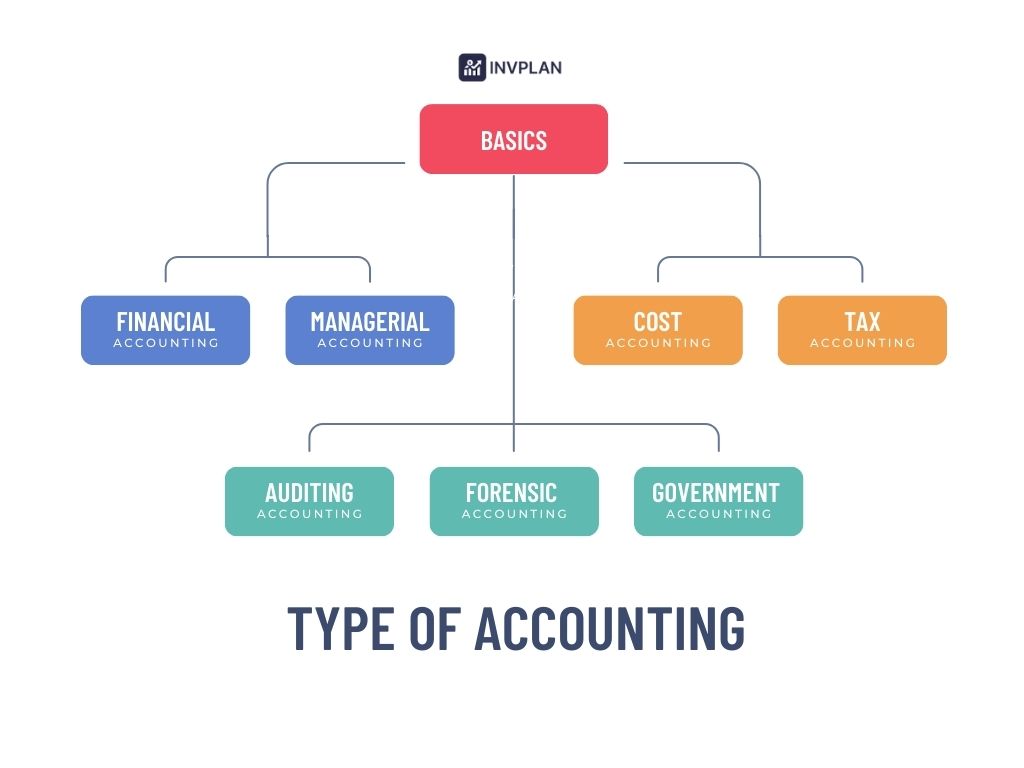
Main Types of Accounting
Accounting has 8 main types, each one has its purpose. Some focus on reporting, while others help companies to make a decision. Here is the list of the eight types:
- Financial Accounting
- Managerial Accounting
- Cost Accounting
- Tax Accounting
- Auditing
- Forensic Accounting
- Government Accounting
- Non-Profit Accounting
Let’s take a look at each one in depth.
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting helps you to handle many things, such as tracking, recording, and reporting your business’s financial transactions. It follows standardized rules to create financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These statements help investors and regulators understand a company’s financial health.
Here are the key aspects of financial accounting:
- Recording transactions helps us to track many accounts, such as: sales, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
- Financial statements are used to summarize financial performance for external use.
- Regulatory compliance to ensure accuracy and transparency in reporting.
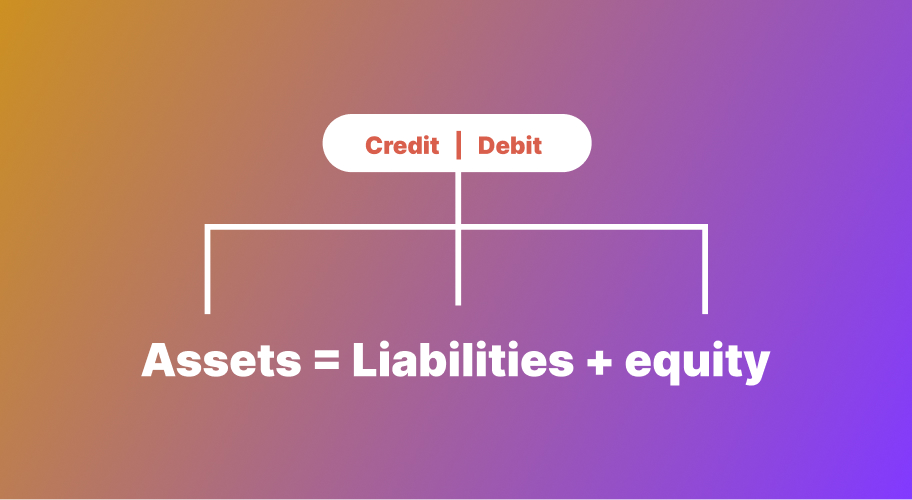
- Double-entry accounting uses debits and credits to maintain balance.
Here is an example of financial statements:
- Income statement shows you many results such as revenue, expenses, and profit over a period.
- A balance sheet lists assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- The cash flow statement tracks cash movement in and out of the business.
Regulatory standards:
Financial accounting follows set rules to ensure accuracy and consistency. The two main standards are:
- Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
- International financial reporting standards (IFRS).
Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting helps businesses make internal decisions by analyzing financial data. It focuses on many processes, such as planning, budgeting, cost analysis, and performance evaluation to improve efficiency and profitability.
Key aspects of managerial accounting:
- It plans the expenses and revenues of the future.
- Divides costs to improve profitability.
- Tracks department and product performance.
- Determines the sales needed to cover costs.
- Helps with pricing and investment to make a decision.
Cost Accounting
Cost accounting helps companies to do many tasks such as track, analyze, and control a company’s costs to improve profitability. It helps you understand how much it costs to produce goods or services and find ways to reduce expenses.
Here are the key aspects of cost accounting:
- It divides costs into many parts such as fixed, variable, direct, and indirect.
- It assigns costs to specific products or departments.
- Compare actual costs to expected costs.
- ABC – This allocates overhead based on activities that drive costs.
- Finds the point where revenue covers total costs.
Tax Accounting
Tax accounting focuses on many tasks such as preparing, filing, and managing taxes according to government regulations. It ensures businesses and individuals comply with tax laws while it minimizes tax liabilities legally.
Here are its key aspects:
- It helps companies in returns and ensures timely payments.
- Cost accounting also determines ways to reduce taxes through deductions and credits.
- Helps companies to track taxes related to sales and business operations.
- It manages differences between accounting income and taxable income.
- It stays updated on changing tax laws to avoid penalties.
Auditing
Auditing examines a company’s financial records to ensure accuracy and transparency. It helps detect errors or fraud in financial reporting.
Audits follow generally accepted auditing standards (GAAS) or international standards on auditing (ISA). A clean audit report builds trust with investors and regulatory authorities.
Here are the types of auditing:
- Internal audit–conducted by in-house auditors to improve operations and risk management.
- External audit–performed by independent auditors to verify financial statements for investors and regulators.
- Tax audit–This ensures tax filings follow government regulations.
- Compliance audit–checks if a company follows industry rules and legal standards.
- Forensic audit–This investigates fraud or financial crimes.
Forensic Accounting
Forensic accounting investigates financial records to uncover fraud or financial crimes. It combines many types of skills, such as accounting, auditing, and investigative skills, to analyze suspicious transactions and provide evidence in legal cases.
Here are aspects of forensic accounting:
- Fraud detection–determines financial fraud and asset misappropriation.
- Litigation support–provides expert financial analysis for lawsuits.
- Financial investigations–examines money laundering or tax evasion.
- Insurance claims analysis–verify legitimacy of claims in fraud cases.
- Business valuation disputes–evaluates financial losses in legal conflicts.
Forensic accountants work with law enforcement and corporate investigators. Their findings help in court cases and fraud prevention efforts.
Government Accounting
Government accounting tracks and manages public funds to ensure transparency and accountability with laws. It focuses on how governments collect and spend money.
Here are its key aspects:
- It tracks money for specific programs or projects.
- It ensures that spending follows legal and regulatory requirements.
- It prepares financial statements for taxpayers and oversight bodies.
- It monitors income from taxes, fees, and grants.
- It evaluates how efficiently public funds are used.
Non-Profit Accounting
Non-profit accounting tracks and reports financial activities for organizations that operate without a profit motive. It ensures transparency and compliance with donor and legal requirements.
Key Aspects of Non-Profit Accounting:
- Separates money into restricted and unrestricted funds.
- Tracks donations that must be used for specific purposes.
- Ensures grants are spent according to funding agreements.
- Includes Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) and Statement of Activities (Income Statement).
- Files tax-exempt reports like IRS Form 990 (in the U.S.).
Let’s move on to the following section to take a look at other different types of accounting.
Specialized Accounting Fields
They focus on specific industries or financial needs or regulatory requirements. These areas help businesses and professionals manage finances effectively.
Each field adapts accounting principles to specific industries and ensures compliance.
Environmental Accounting
It tracks the financial impact of a company’s environmental activities. It helps businesses measure costs related to pollution and sustainability efforts while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Environmental accounting helps businesses balance profitability with sustainability and improve their corporate reputation.
- Environmental cost analysis–tracks costs for waste management and sustainability programs.
- Carbon accounting–measures greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint.
- Regulatory compliance–ensures discipline to environmental laws and reporting standards.
- Sustainability reporting–discloses environmental impact in corporate reports (e.g., ESG reports).
International Accounting
International accounting deals with the financial practices and regulations that apply across different countries. It ensures companies can report and manage finances globally, it complies with various rules and standards.
Project Accounting
Project accounting tracks and manages the financial performance of specific projects within a business. It helps ensure that a project stays within budget and meets its financial goals.
It ensures that every project stays financially on track. And helps businesses assess profitability and make informed decisions about future projects.
How to Choose the Right Type of Accounting for Your Business?
It depends on many factors, such as your goals, industry, size, and specific financial needs. Here’s how to decide:
1- Identify your business type
- For-profit businesses need financial and managerial accounting for internal and external reporting.
- Non-profits require non-profit accounting to manage donations and grants.
- Government entities need government accounting to handle public funds and ensure compliance.
2- Consider your financial needs and growth
- Tax accounting is important to manage tax and planning.
- Cost accounting helps if your business needs to track production or operational costs closely.
- Project accounting is ideal for businesses with project-based operations (e.g., construction or consulting).
3- Industry-specific requirements and Legal considerations
- Healthcare and retail each have specialized accounting fields that help manage specific financial needs.
- International businesses should consider international accounting for handling cross-border regulations and currencies.
Wrapping Up
Accounting is important for all businesses, and the type you use will depend on your industry and financial requirements. So if you are looking into many aspects like financial reports, cost, tax, and project tracking, detailed accounting serves you in different ways as it caters to specific needs.
In this article, we discussed the different major types of accounting: financial, managerial, cost, tax, auditing, forensic, government, and non-profit accounting.
Selecting the best accounting system depends on understanding the specific needs and growth potential of your business.
For more information, click here to learn more.