Many startups struggle with a common challenge—so, build a business model that works without a clear plan even the best ideas can fail.
Many entrepreneurs focus on their product or service but overlook how they will create, deliver and capture value. Without structure, it’s easy to waste time and lose money..
In this article, we will cover the following topics:
- Steps to create a business model for start-ups.
- Difference between business model and business plan.
- How to validate your business model.
- Tools and examples of business models in start-ups.
Before we get started, take a look at this article to understand what a business model is and its case studies. Let’s move on to the following section to learn how to create a business model for start-ups.
Building a Winning Business Model
There are 9 steps to design a business model for startups, let’s see each one in details:
1- Identify Customer Segments
Your customers define your business. Understanding them helps you create better products and services. There are different types of customer segments, such as:
- Mass markets—broad audiences with general needs.
- Niche markets—smaller and specialized groups with unique demands.
- Segmented markets—similar groups with slight differences in preferences.
- Diversified markets—completely different customer bases served by the same company.
- Multi-sided markets—buyers and sellers connecting on a platform.
Build an Ideal customer profile to target the right people and define their demographics, interests, and behaviors. Then, Develop a buyer persona that outlines their goals and purchasing habits.
2- Define Your Value Proposition
Customers need a reason to choose you over competitors. So, a strong value proposition makes that reason clear. You have to ask yourself about the following questions:
- What problem does your product solve?
- How does it make life easier or better?
- What makes it different from the competition?
Use the value proposition canvas to refine your offer.
- List customer needs to know what they expect from a solution.
- Identify pain points—challenges they face.
- Highlight desired benefits and what they truly want.
- Match these with your product’s key features.
The closer your solution aligns with their needs, the more compelling your value proposition becomes. Show customers why your product matters and they will choose you.
3- Choose Your Channels
Businesses typically use two types to reach customers that requires the right channels:
- Direct channels: selling through company that owned stores—or websites or sales teams.
- Indirect channels: debends on third-party such as retailers, marketplaces or distributors.
Each option has trade-offs.
So, direct channels offer control but require more effort.
Indirect channels increase reach but reduce profit margins. You need to balance cost with convenience and customer behavior.
Digital marketing expands visibility. So, you have to consider these strategies:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization) customers find you online.
- Social media to engage audiences and build brand awareness.
- Email marketing to nurture leads and drive repeat purchases.
- Paid advertising to attract targeted buyers quickly.
Use the channels that best fit your product and audience to make buying easy.
4- Map Customer Relationships
Customers return when they feel valued. Within this there are two main ways to engage with them:
- Personal interactions such as customer support, direct communication, and personalized service.
- Automated interactions like self-service portals, AI chatbots, and email automation.
Focus on three key areas to build loyalty:
- Customer support—responsive service builds trust and helpful.
- Loyalty programs—encourage repeat purchases such as discounts, rewards, and perks.
- Community engagement—create stronger connections by using social media groups or events.
Every audience is different. Some prefer human interaction while others want quick digital solutions. The key is understanding what works best for your customers.
5- Define Revenue Streams
There are multiple ways to generate revenue for a business needs a fixed income:
- Subscriptions—customers pay regularly for continued access (eg., Netflix, software memberships).
- One-time purchases—traditional sales of goods or services.
- Licensing fees—charing others to use your technology or brand.
- Advertising revenue—eran from third-party promotions on your platform.
Pricing also affects success. Consider different models:
- Cost-based pricing—cover expenses plus a profit margin.
- Value-based pricing—charge based on customer perception of worth.
- Demand-based pricing—adjust prices according to market trends.
A solid revenue model keeps your business profitable and sustainable.
6- Identify Key Resources
Your business relies on essential resources to operate. These include:
- Physical assets—offices with warehouses, and equipment.
- Intellectual property—patents—and trademarks and proprietary technology.
- Human resources—skilled employees and leadership teams.
- Financial resources—funding—and investments and cash flow.
Prioritizing resources strengthens your competitive edge. Invest wisely to sustain growth and long-term success.
7- Plan Key Activities
Successful businesses focus on essential activities. Your company must:
- Innovate and refine offerings—(Develop products ).
- Create brand awareness and attract customers.
- Convert leads and build loyalty.
- Address customer pain points and improve operations.
Every business has different priorities. Some focus on product development while others emphasize customer relationships. The key is to concentrate on activities that drive results.
8- Establish Key Partnerships
Partnerships strengthen businesses. There are three main types:
- Strategic alliances—collaborations with non-competitors to expand capabilities.
- Joint ventures—shared business projects for mutual gain.
- Supplier agreements—ensuring reliable access to materials and products.
Good partnerships lower costs increase reach and improve efficiency. Choose partners that align with your goals and enhance your business operations.
9- Build a Cost Structure
Managing costs is critical for profitability. Businesses face two main types:
- Fixed costs—expenses that remain constant such as rent and salaries.
- Variable costs—fluctuating expenses like raw materials and marketing.
A cost-effective business minimizes waste without sacrificing quality. Key strategies include:
- Streamlining operations—cutting unnecessary expenses.
- Negotiating better supplier rates—reducing material costs.
- Investing in automation—saving on labor and increasing efficiency.
Balancing expenses with value delivery ensures long-term success. A well-structured cost plan keeps your business financially stable and scalable.
In the below section, you will learn 24 types of business models from the top. let’s move on.
Types of Business Models
Many companies use a mix of the following models to stay competitive and meet customer needs. The key is to choose the one (or a combination) that aligns with your goals.
Here is a list of common types of business models:
- Subscription Model.
- Freemium Model.
- E-commerce Model.
- Marketplace Model.
- Advertising Model.
- Direct Sales Model.
- Franchise Model.
- Razor and Blades Model.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Model.
- On-Demand Model.
- Brick-and-Mortar Model.
- Drop Shipping Model.
- Affiliate Model.
- Crowdfunding Model.
- Licensing Model.
- Pay-As-You-Go Model.
- Bundling Model.
- Agency Model.
- Leasing Model.
- Non-profit Model.
- Blockchain/Decentralized Model.
- Rental Model.
- White Label/Private Label.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Model.
- Social Enterprise Model.
To learn more about the types of business models, visit this article. Let’s move on to the following section to learn how to create a business model for a startup.
Now, let’s discuss the difference between a business model and a business plan.
Difference between business model and business plan
A business model explains how the company makes money. That shows who the customers are and why they buy from you and how you deliver value. So, you waste time and money without a clear business model.
You need to know a few key things:
- Who buys from you? Are you serving a broad market or a niche group?
- Why do they buy? the product must solve a problem or offer something better than competitors.
- How do they find you? Do you sell directly through a website or using third-party platforms?
- Where does the money come from? Sales or licensing—or subscriptions. The revenue streams define the business.
A business plan is different. It’s a detailed document that lays out how the business will grow and succeed. Investors care about this. Banks won’t lend money without it.
the business plan should cover:
- What the business does – A clear mission and vision.
- Who else is in the market – Competitors, trends, and customer demand.
- How you’ll attract buyers – Marketing strategies and sales tactics.
- How much money you’ll need – Budgets, revenue projections, and costs.
Here’s the difference—the business model is the foundation. It’s simple. the business plan is the blueprint. It’s detailed and structured. Both matter but they serve different purposes.
Here is a table that shows you the key differences:
| Feature | Business Model | Business Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Describes how a business makes money. | Provides a full roadmap for operations and growth. |
| Detail Level | High-level framework. | In-depth strategy document. |
| Flexibility | Easy to adjust and update. | More structured and detailed. |
| Usage | Internal strategy and brainstorming. | Used for securing investments and guiding operations. |
Let’s move on to the following part to understand the business model canvas.
How to use a business model canvas?
A Business Model Canvas helps you map out how your business works. It’s a one-page tool that breaks everything into nine sections. You get a clear, visual layout of your strategy Instead of writing long plans.
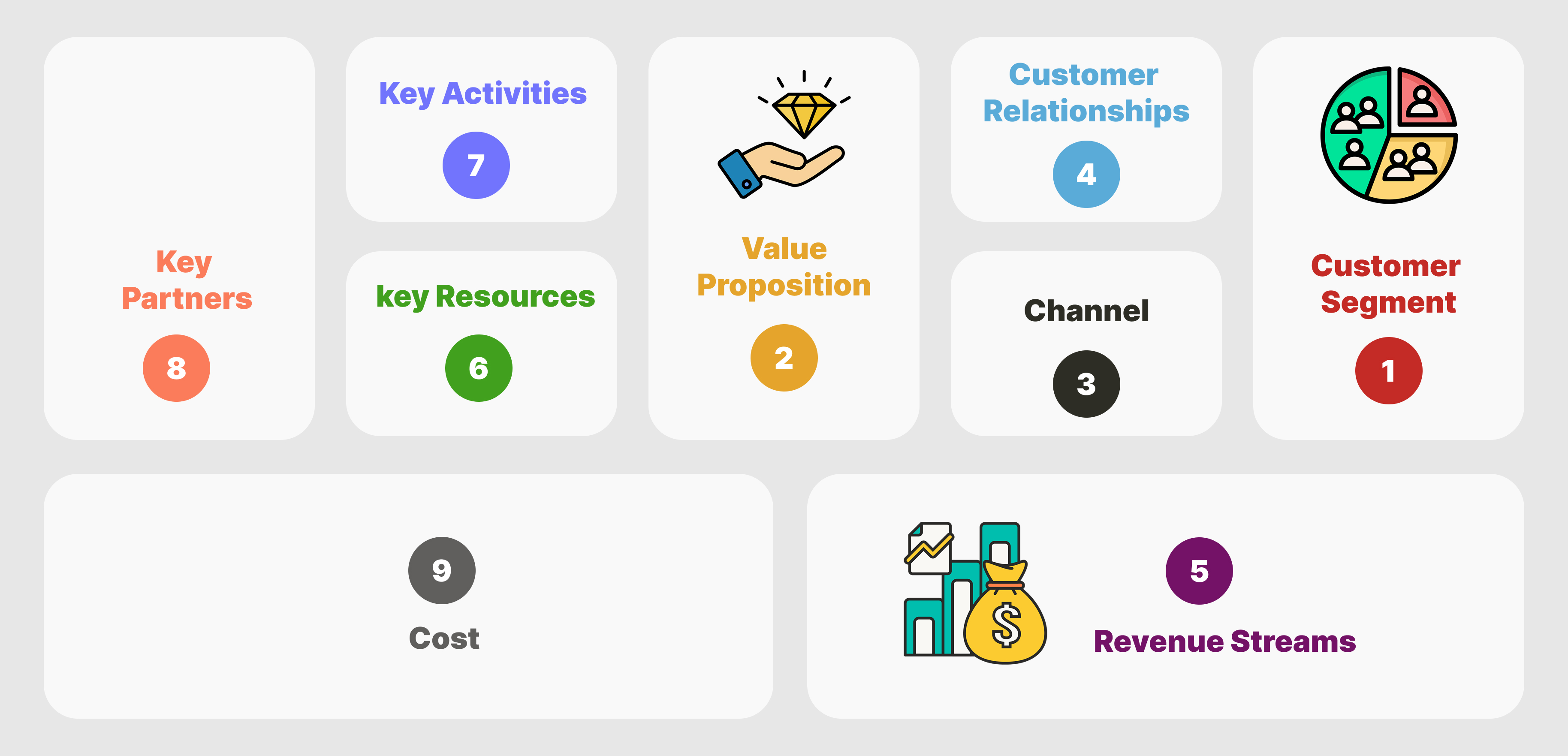
How to Use It?
- Customer Segments – Who buys from you? List the different groups you serve. Some businesses focus on a niche, others have multiple customer types.
- Value Proposition – Why do they buy? What problem does your product solve? What makes it better than alternatives? Be clear and specific.
- Channels – How do you reach your customers? Do they find you through social media, a website, a physical store, or distributors? Write down every way you connect with them.
- Customer Relationships – How do you interact with customers? Is it personal, automated, or self-service? A strong relationship keeps them coming back.
- Revenue Streams – How does money come in? Direct sales, subscriptions, licensing, or ads? Identify every source of income.
- Key Resources – What do you need to operate? This includes equipment, patents, employees, or funding. Focus on what’s essential.
- Key Activities – What actions keep your business running? Think about product development, marketing, customer service, and sales.
- Key Partnerships – Who helps your business? This could be suppliers, distributors, or strategic allies that provide resources or customers.
- Cost Structure – Where does the money go? List fixed costs like rent and salaries—then variable costs like materials or marketing.
In the following section, you will learn how to validate your business model. Let’s move on.
How to Validate Your Business Model
Test ideas before you commit.
- Ask people if they would pay and watch their reactions.
- See if they hesitate and find out why.
- Track what they do not just what they say.
Build something simple first.
- Use a basic version to check demand.
- Keep costs low and launch fast.
- Let customers try it and watch if they return.
Sell before you scale.
- Take small steps to test if people will pay.
- Set up an easy way to buy.
- Track repeat sales and strong demand means no extra push.
Check real numbers not guesses.
- Count users and buyers and repeat customers.
- Fix problems if growth slows.
- Watch what works. Do more of that.
Tools & Templates to Create a Business Model
Use tools that help you plan. A business model canvas breaks ideas into key parts. Spreadsheets track costs and revenue. Surveys collect customer feedback. Just pick simple tools that keep you focused.
Templates save time and add structure. A one-page business plan highlights key details. Financial forecast templates help plan expenses. Before launch, customer journey maps show how people interact with your product. These tools help you adjust early.
Test ideas before you commit. A/B tests compare different options. Prototypes check if people want your product. Market research reports reveal demand. Track key numbers with dashboards and change plans based on real data.
Wrapping Up
A strong business model keeps a company focused and profitable. Without structure, even great ideas fail. Defining customer needs and revenue streams with key activities helps businesses operate.
Testing is just as important as planning. Watch how customers respond and track real number. Small tests save time and money before scaling.
Use the right tools to stay organized. Business model templates and customer feedback tools make planning easier.
FAQ’s
How should I update my business model?
- Update your business model by tracking real data and adjusting based on results. Test customer behavior-monitor revenue streams, and see what works. find the cause and fix it fast If sales drop or costs rise.
- Improve how you reach customers. Refine marketing and adjust pricing if needed. Keep your value clear and relevant. If customer needs shift you need to adapt your product or service.
- Use tools to stay organized. A business model canvas helps visualize changes. Financial tracking shows profit trends. Customer feedback highlights what to improve.
Can I change my business model after launching?
Which business model is best for a startup?
How do I create a business model for my business?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a business model?
A business model explains how a company makes money. It defines the customers, value proposition, revenue streams, and key operations.
A business plan is a detailed roadmap for growth. It includes goals and marketing strategies, financial projections and operational plans. Investors and banks use it to assess the business.